Electrostatic Filters (ESP)
Filters
Industrial filter systems provide to remove particulates (dust, smoke, fiber) and gases that cause unhealthy and undesirable conditions by collect. Filter systems provide to recover recyclable material and keep clean factory enviroment, and on the other hand remove excessive heat and humidity. Air cleaning devices pickup pollutans from the air and gas stream. Filters have a wide range of design types to provide the requirement of different air. The required degree of cleaning, the amount and properties of the pollutant, the conditions of the air or gas flow will be effective in selecting the cleaning device to be used for the application. Also, in must be taken to attention fire security and explosion control in selecting device.
The filter types that used in industry widenly;
- Jet - Pulse Filter
- Cyclones - Filters
- Electrostatic Filters
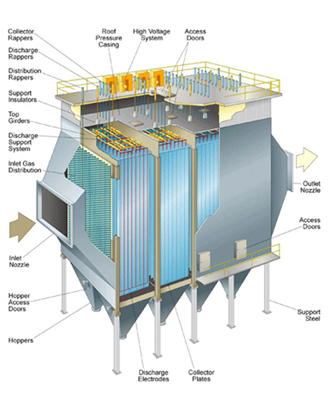
Electrostatic Filters (ESP)
One method of increasing the particle holding capacity of air filters without increasing the fiber density is electrostatic filters. Active electrostatic filters, by taking advantage of the high income generated between the plates, ensure the retention of loaded particles. These filters have a very high particle holding capacity. Despite their high performance, their assembly and operating costs are quite high. They are not preferred for small domestic and commercial applications due to their high cost.
Another method developed to contain particles by deactivating the high voltage field in active electrostatic filters (thus reducing other costs) is passive electrostatic filters. General working principle; The air is sucked by the motor / blower through a metal mesh pre-filter that holds large dust particles. Among the remaining particles, those with a size of 0.01 micron pass into the strong electrical field where they are charged with electric charge. The charged particles pass into the collector plate part made of equally spaced parallel plates. The plates attached to the gap was earthined. Thus, it pulls and collects particles. Each plate that follows each other in turn is electrically charged at the same polarity as the particles. Therefore , it repels particles.
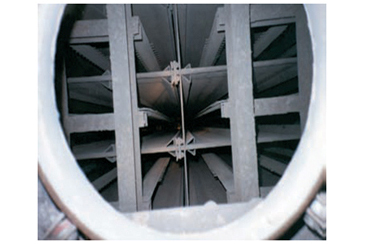
In these systems, we create a cleaning effect with our Sonic horn system. Thus, we prevent the destructive damage that occurs over time by removing the hammer method in ESP for the fly ash accumulated on the plates.
Condition observed when sonic horn is not active.

Condition observed when sonic horn is active.

6 weeks after production without sonic cleaning. Dust emission 29.4 mg/Sm

6 weeks after production with sonic cleaning. Dust emission 13,5 mg/Sm
Compared to the known technique, our system is a much more efficient and economical system.
