User Explosion Pulse Cleaning

What is EPC?
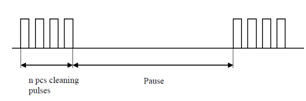
The system has been developed to eliminate difficult particles adhering to each other and to the surface with shock waves. User Explosion Pulse Cleaning system creates a shock wave and cleans the slag in areas such as high temperature superheater. When the system is online, the system runs in a periodic cleaning cycle. It is the best solution in the field for the elimination of difficult particles.
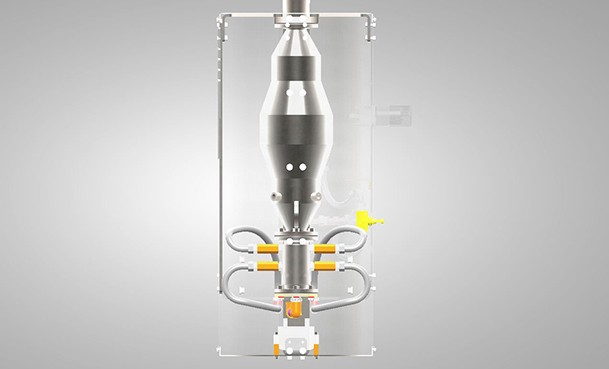
The system has been developed to eliminate difficult particles adhering to each other and to the surface with shock waves. User Explosion Pulse Cleaning system creates a shock wave and cleans the slag in areas such as high temperature superheater. When the system is online, the system runs in a periodic cleaning cycle. It is the best solution in the field for the elimination of difficult particles.
Also, the gas used as fuel is obtained from the gas source used to ignite the boiler's burners. (propane, natural gas etc.)
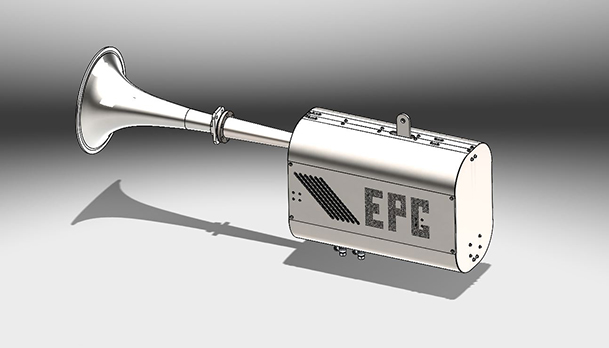
The system consists of 6 main parts;
- Actuator (Çalıştırıcı)
- Horn (Korna)
- Pneumatic Units (Pnömatik Ekipmanlar)
- Gas Units (Gaz Ekipmanları)
- Ignition System (Ateşleme Sistemi)
- Electric Apparatus ( Elektrikli Cihazlar)
If we briefly define the working principle of the system; The fuel and air that we will obtain the energy that will be effective on the slags are mixed in a certain ratio. This mixture is ignited in milliseconds in the combustion chamber. Thus, the chemical energy of the fuel is converted into kinetic energy. This kinetic energy creates a large pressure increase in the combustion chamber. Thanks to the idealized horn structure that opens from the combustion chamber to the outside, this energy accelerates and emerges as a shock wave. The horn structure at the exit not only contributes to the shock wave formation, but also gives it a certain frequency. As a result, a shock wave that behaves differently from the normal sound wave with a sound power of approximately 170 dB is formed.
Some of the characteristic features of shock waves are as follows;
- Their speed is higher than approximately 344 m / s. Ma> 1
- The thickness of a standard shock wave in atmospheric air is 2.5 angstroms. ( 1 angstrom = 1.0 ×〖10〗^(-10) metre = 10 milimicron )
- Shock waves are irreversible, discontinuous and nonlinear waves.
- As shock waves advance, pressure, density, entropy, temperature, velocity rise and fall suddenly.
- When we compare a 170 dB shock wave with a 130 dB acoustic sound wave, the shock wave effect is 1020 times greater than the effect created by the acoustic wave.
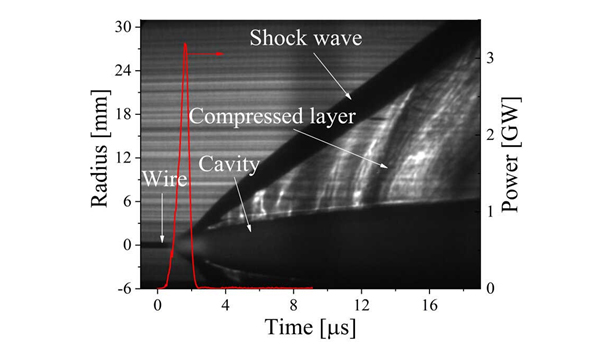
THE IMPACT OF SHOCK WAVES ON SLAG
User Explosion Pulse Cleaning can generate approximately 10-15 explosion per second. Every explosion means a shock wave. The high density and sharp shock wave generated in this online system directly affects the slag in the heat exchanger tubes.
Among the features mentioned above, the shock waves have a very thin and dense structure, causing them to have a cutting effect on the slag. Thus, the slag will split into pieces and break off the surface. (mechanical effect of shock wave)

Thermal stresses occur due to the sudden change in temperature, pressure, density and entropy in the areas where shock waves pass. These sudden thermal stresses again weaken and facilitate the breakdown of molecules in the slag structure. (shock waves thermal effect)
The impact of shock waves on slag has many positive effects. Shock waves generated by USER - EPC are reflected to tube bundles. Due to the reflections that occur, a cleaning effect occurs even in inaccessible areas of the tubes (behind the tubes). Shock waves are reflected in the voids in the structure of the slag beside the reflections between the tube bundles. thus contributes to the slag breaking down easily. (mechanical effect of shock waves)
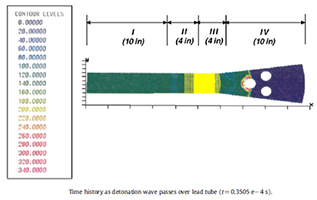

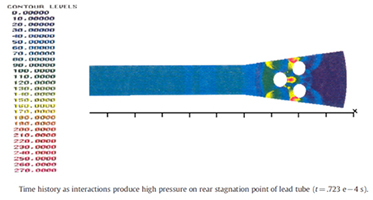
Due to the shock waves delivered in pulses, the velocity of the flow flowing between the tube bundles constantly increases to supersonic level. Then it returns to the subsonic level. These repetitive changes create a scrubbing, sweeping effect on the tube packages. This effect allows the slag surrounding the tube bundles to be disposed of. (mechanical effect of shock waves)
As explained above, shock waves have a very high slag removal capacity. Besides, it has no corrosive effect on the tube packages and the boiler. Chemical energy transformed into kinetic energy is not high enough to adversely affect boiler materials. In addition, the frequency of operation is low compared to other cleaning methods. This is again advantageous in terms of no negative effects.
